Basically, financial reporting provides a means to measure your financial performance. While financial performance may not be your ultimate measure of success, it is an important measure for the sustainability of your business.
The 3 Basic Financial Reports
The three basic financial reports and some metrics they contain are provided as follows:
| Financial Statement | Metrics |
| Profit & Loss | Sales Revenue, Total Expenses, Net Profit |
| Balance Sheet | Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Owner Investments, Owner Distributions, Total Equity |
| Cash Flow | Net Cash Increase during Period, Cash at end of Period |
The 4 Types of Money
In The E-Myth Accountant (Gerber 2011), Michael Gerber describes four types of money: Income, Profit, Flow, and Equity. Each type of money serves a purpose for you as a business owner. Firstly, Income is what pays your salary. You find the Income for your business at the top of your Profit & Loss statement in the Sales Revenue line item. Secondly, profit fuels company growth and/or owner distributions. You find Profit towards the bottom of your Profit & Loss statement in the Net Profit line item. Thirdly, flow is what money does for your business (and how a lack thereof can bring your business to a quick and speedy end). You find information regarding the flow of money through your business in the Cash Flow statement. Finally, Equity is the value of the business you are building. You find the Total Equity of your business towards the bottom of your Balance Sheet.
Strategic Metrics
Undoubtedly, certain types of money will be in conflict. For example, you cannot simultaneously maximize your salary, (an expense) and your Equity, because expenses inherently reduce your retained earnings. In order to build a successful, sustainable business, you must find a strategic balance as you manage each type of money. As an aid to striking a strategic balance, you may set targets for certain types of money, e.g., you may set your target compensation (or salary) to be a certain percentage of your Income. The point here is that financial reporting is important, because it provides important, strategic metrics regarding the types of money that are important to your business.
Financial Reporting Requirements
Your accounting software should be capable of generating the three basic financial reports: Profit & Loss, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow. These reports should be generated at the end of each accounting period (usually at the end of the month), after reconciling your accounts for the same period. Once generated, metrics within these reports should be compared with target metrics and tracked over time, in order to compare performance with previous periods. In addition to generating and reviewing the basic financial reports, a financial reporting application may be connected to your accounting software and configured to facilitate reporting on important metrics specific to your business.
Financial Reporting Roles & Responsibilities
Reporting & Analysis is the responsibility of the reporting administrator, as communicated in the following overview diagram for cloud-based bookkeeping roles & responsibilities. Depending upon your staffing strategy, the firm manager and reporting administrator roles may be delegated to one or more employees. Alternatively, you may decide to outsource the reporting administrator role to an outsourced bookkeeper or accountant.
Financial Reporting Concept of Operations
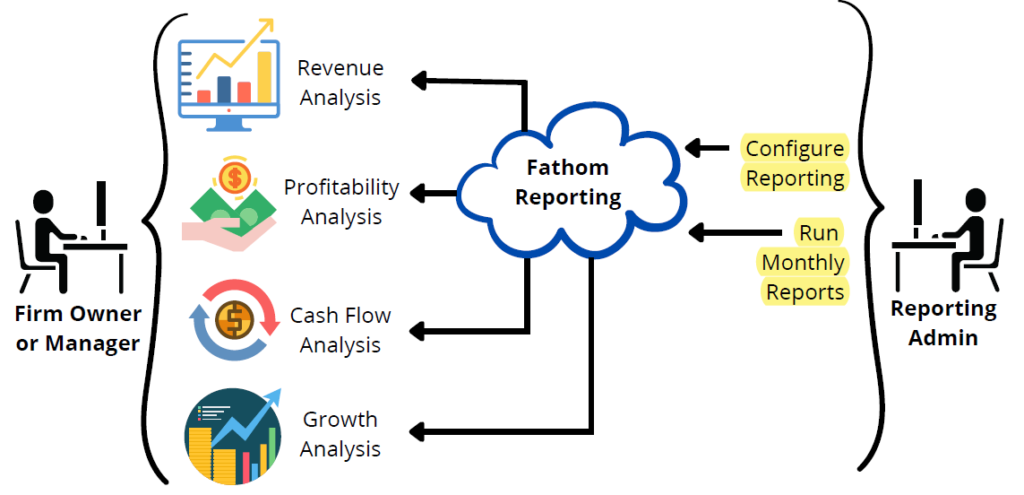
Now consider the following concept of operations for financial reporting. You are using QuickBooks online accounting software and your reporting administrator is generating monthly financial reports, including your P&L, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement. In order to track financial metrics over time and access analysis for revenue, profitability, cash flow, and growth, the reporting administrator integrates your QuickBooks account with Fathom, a cloud-based financial reporting & analysis application.
Key Performance Indicators
Your reporting administrator configures Fathom to report on key performance indicators for your design firm, including revenue, profit margin, accounts receivable days, utilization rate, quick ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, free cash flow, and backlog volume. Then, each month, a line chart indicates the value of each key performance indicator over the past twelve months.
Revenue Analysis
Firstly, a revenue analysis shows your actual monthly revenue versus your target monthly revenue over the past twelve months and your revenue mix (e.g. preliminary design revenue, design development revenue, construction documents revenue, construction administration revenue) over the same period.
Profitability Analysis
Secondly, a profitability analysis provides a breakeven analysis, with a margin of safety that indicates the gap between actual revenue and your breakeven point. The profitability analysis also includes a line chart that plots revenue and expenses over the past twelve months.
Cash Flow Analysis
Thirdly, your cash flow analysis reports on operating cash flow, net cash flow, and free cash flow, with a bar chart that demonstrates how each metric is calculated as a compilation of different types of cash received and cash spent.
Growth Analysis
Finally, a growth analysis shows earnings vs. operating investment for the current period vs. the previous period, with four performance categories: efficiency gains, quality growth, decline, and stress. In general, you like the visual aspect of the charts and graphs reported using Fathom, because they make the metrics from your basic financial reports easier to comprehend.
Financial Reporting Workflow
The Financial Reporting Workflow immediately follows the Account Reconciliation Workflow during the month-end processing. You may choose to manage your workflows, using a cloud-based application. The one I use is 17hats.
Report Workflow
| Step | Description |
| 1 | Prepare Balance Sheet – Run and save the balance sheet, using QuickBooks standard reports. |
| 2 | Prepare Profit and Loss – Run and save the profit and loss, using QuickBooks standard reports. |
| 3 | Prepare Statement of Cash Flows – Run and save the statement of cashflows, using QuickBooks standard reports. |
| 4 | Perform Financial Analysis for Revenue, Profitability, Cash Flow, and Growth – Create a Monthly Performance Report, using the standard template in Fathom. |
| 5 | Close Books – Go to the Advanced tab under Account and Settings in QuickBooks. Under Accounting, select ‘Close the Books’, and enter the date for the end of the period. |
| 6 | Re-schedule Account Reconciliation Workflow for the Next Period – When the Report Workflow is complete, re-schedule the Account Reconciliation Workflow for the next period. |
Referenced Applications
To learn more about the applications referenced in this post, please click the following external links:
- Accounting Software, QuickBooks Online (QBO): https://quickbooks.intuit.com/
- All-in-One Small Business Management Platform, 17hats: https://www.17hats.com
- Financial Analysis Software, Fathom: https://www.fathomhq.com/
Subscribe to Learn More
Improve efficiencies at your architecture, engineering, or design firm by subscribing to this blog. Specifically, the blog provides hints and tips for the administration of Cloud Accounting, Payroll Services, and Professional Services Automation. When you subscribe, you get notifications when new posts are published. To subscribe to this blog, enter your email in the block below, and click the Subscribe button.
Explore Other Blog Posts
References
Gerber, Michael E. (2011). The E-Myth Accountant: Why Most Accounting Practices Don’t Work and What to Do About It, Chapter 3, On the Subject of Money.



